- Compound Fertilizer Production Line
- Grinding Equipment
- Material Feeding Equipment
- Dust Collection Equipment
- Drying Equipment
- Conveying Equipment
- Elevating Equipment
- Crushing Equipment
- Screening Equipment
- Industrial Mixing and Agitation Equipment
- Granulation Equipment
- Calcination Equipment
- Cooling Equipment
- Bulk and Packaging Equipment
Cooling Equipment Supplier
Cooling equipment is a critical component used in industrial production, commercial operations, and everyday life to reduce the temperature of materials, equipment, or the environment. Its core function is to transfer heat from the object to be cooled to the external environment or a cooling medium (such as water, air, or refrigerant) through specific heat transfer methods (such as conduction, convection, and radiation). This allows for temperature control, ensuring stable production processes, normal equipment operation, and meeting the temperature and humidity requirements of a specific space.
In terms of application, cooling equipment covers a wide range of industries, including but not limited to the building materials industry (such as material cooling in cement and lime production), the metallurgical industry (such as cooling high-temperature materials after metal smelting), the chemical industry (such as removing heat during chemical reactions), the power industry (such as cooling generator sets), and the food processing industry (such as cooling and preserving food). Within different industries, cooling equipment has evolved into various types, depending on the form of the cooling object (solid, liquid, gas), temperature requirements, processing capacity, and operating environment conditions. Common types include chillers and air coolers. Each type of equipment has specific differences in structural design, operating principles, and performance parameters to meet the cooling needs of different scenarios.

-
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Compound Fertilizer Production Line The efficiency of the Compound Fertilizer Production Line is influenced by various factors, which can significantly impact production output, quality, and overall operational costs. Understanding these factors is crucial for man...
READ MORE -
The capacity of a compound fertilizer production line plays a crucial role in determining its operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall productivity. Understanding how to calculate and select the right capacity is essential for manufacturers looking to meet market demand while maintain...
READ MORE -
Establishing a compound fertilizer production line is a complex task that requires careful planning, proper site selection, and construction of the right facilities. This involves evaluating the physical space, technical infrastructure, environmental factors, and ensuring compliance with regulations...
READ MORE
Cooling Equipment is used in fertilizer and building materials production lines to reduce product temperature after drying, granulation, or calcination processes. Typical applications include compound fertilizer, organic fertilizer, and BB fertilizer production, where Cooling Equipment helps stabilize finished granules, improve storage performance, and enhance downstream screening and packaging efficiency. As a long-term manufacturer of fertilizer machinery, Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. incorporates Cooling Equipment into complete production systems to support stable and continuous operation.
1. Working Principles of Cooling Equipment
Different types of Cooling Equipment share the goal of reducing material temperature, but their structural forms and cooling mechanisms vary:
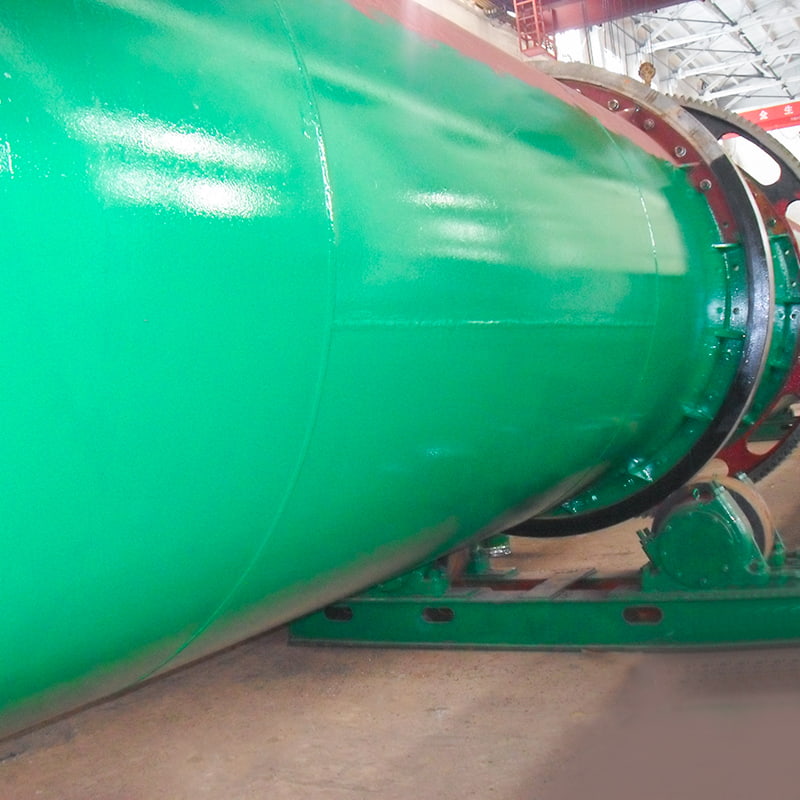
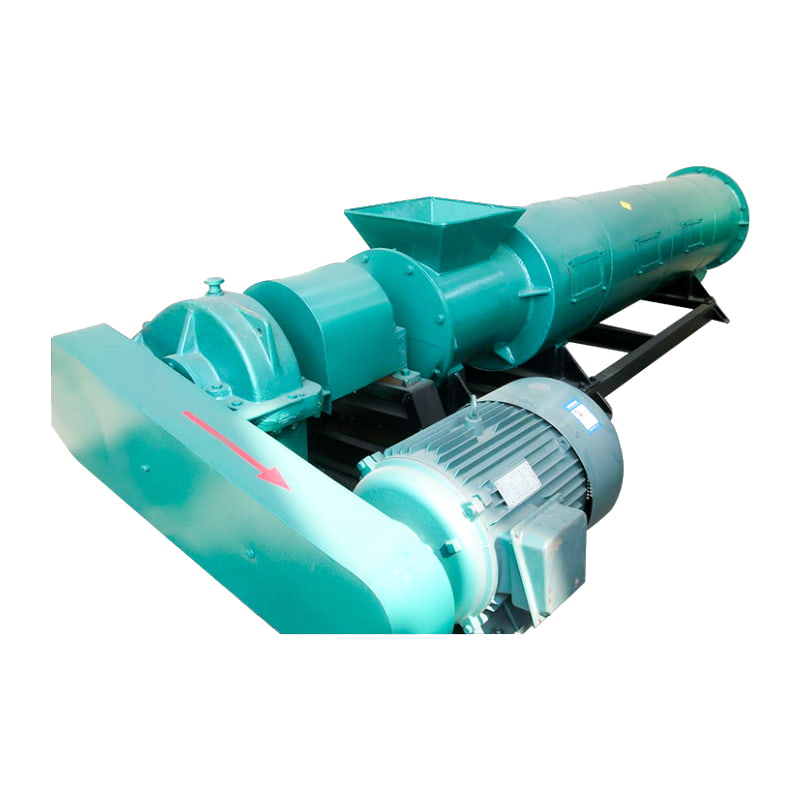
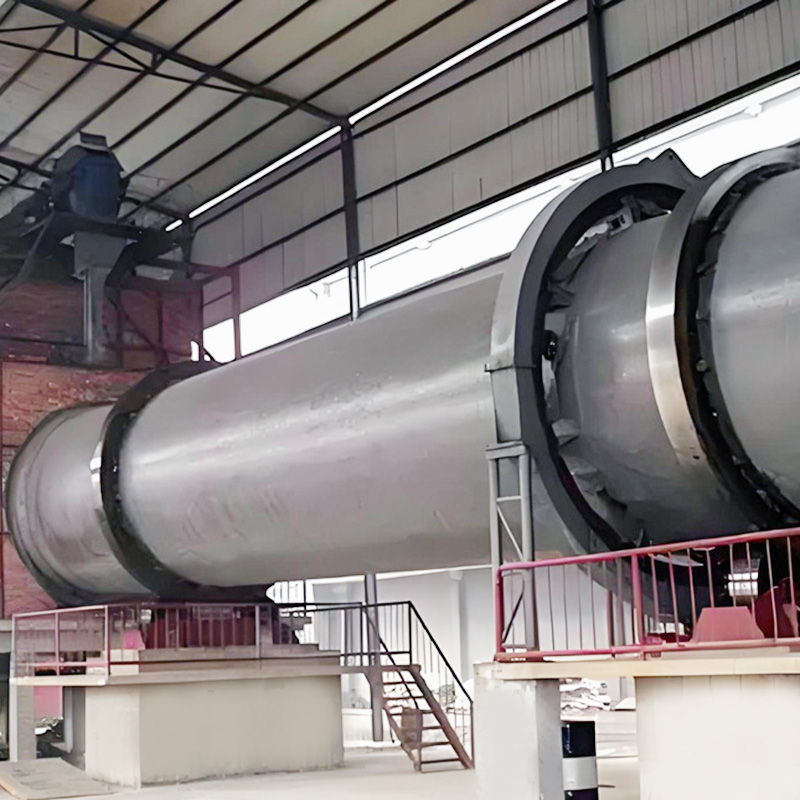
(1) Rotary Drum Cooler
-
Principle: Uses counter-flow or co-current air contact in a rotating cylinder to exchange heat with hot granules.
-
Features: Large treatment capacity, suitable for high-throughput fertilizer lines.
-
Typical Use: Cooling compound fertilizer granules after drum drying and granulation.
(2) Fluidized Bed Cooler
-
Principle: High-velocity air causes material to form a fluidized layer, enhancing uniform heat transfer.
-
Features: Suitable for small-size or uniform granules with strict cooling requirements.
-
Typical Use: Fine chemical materials or granules requiring precise thermal control.
(3) Airflow Cooler
-
Principle: Uses large-volume ambient air to cool light or powder-type materials through suspension and airflow contact.
-
Features: Effective for powders or materials with low mechanical strength.
-
Typical Use: Cooling organic fertilizer powder or lightweight granules.
2. Comparative Overview of Cooling Equipment
| Equipment Type | Applicable Material | Cooling Efficiency | Capacity Range | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Drum Cooler | Medium–large granules | High | Large | Stable operation; low maintenance |
| Fluidized Bed Cooler | Uniform, small granules | Very high | Medium | Precise temperature control |
| Airflow Cooler | Powder or light material | Medium | Medium–large | Low energy use; simple structure |
In production lines provided by Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., drum coolers are frequently paired with rotary dryers and granulators to form a closed, continuous granulation process.
3. Application Examples
Example 1: Compound Fertilizer Production Line
Cooling Equipment reduces NPK granule temperature from 70–90°C to near ambient temperature, preventing caking during storage. Rotary Drum Coolers are commonly integrated after drying systems.
Example 2: Organic Fertilizer Plant
For materials with high moisture content, airflow coolers are used to cool semi-finished powder before screening to maintain particle structure.
Example 3: Potassium Sulfate Processing
Fluidized bed coolers support efficient and uniform cooling of crystalline materials to ensure product stability.
4. Maintenance Guidance for Cooling Equipment
To ensure long-term stable performance, users should follow routine maintenance guidelines:
Rotary Drum Cooler
-
Check cylinder sealing and prevent air leakage.
-
Inspect riding rings, rollers, and drive components.
-
Keep internal lifting plates free of buildup.
Fluidized Bed Cooler
-
Maintain uniform air distribution plates.
-
Clean dust from air ducts and fans regularly.
-
Check vibration parameters and support structure.
Airflow Cooler
-
Ensure air volume and air temperature remain stable.
-
Inspect cyclone separators and dust removal connections.
-
Monitor wear on pipelines in high-velocity airflow zones.
5. FAQ for Cooling Equipment
Q1: How to determine which Cooling Equipment is suitable?
A selection is based on particle size, moisture content, airflow requirements, and overall capacity of the production line.
Q2: Can Cooling Equipment be connected to existing dust collection systems?
Yes. Many systems from Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. integrate with dust collectors to reduce airborne dust.
Q3: What temperature should the material reach after cooling?
Typically within 5–10°C of ambient temperature to ensure storage stability.
Q4: Do different Cooling Equipment types require different air volumes?
Yes. Drum coolers need moderate air volume, while fluidized bed coolers require high-pressure air for fluidization.
Q5: How often should cleaning and inspection be performed?
Routine inspection is recommended weekly; comprehensive maintenance monthly.

 En
En
 English
English  Français
Français  русский
русский  中文简体
中文简体  عربى
عربى  Español
Español