- Compound Fertilizer Production Line
- Grinding Equipment
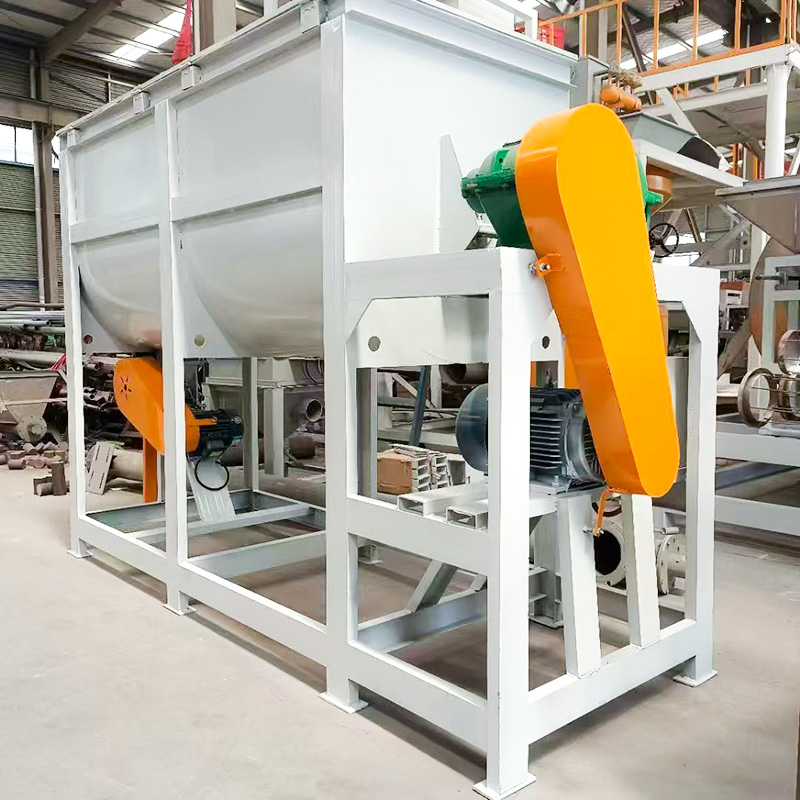
- Material Feeding Equipment
- Dust Collection Equipment
- Drying Equipment
- Conveying Equipment
- Elevating Equipment
- Crushing Equipment
- Screening Equipment
- Industrial Mixing and Agitation Equipment
- Granulation Equipment
- Calcination Equipment
- Cooling Equipment
- Bulk and Packaging Equipment
Fertilizer Granulation Equipment Supplier
Granulation equipment is a key component of material granulation in industrial production. It transforms dispersed raw materials into granules of a specific size and strength through physical or chemical reactions. This not only facilitates material storage, transportation, and metering, but also improves subsequent processing efficiency and product quality. It is widely used in fertilizers, metallurgy, building materials, and other fields. For example, granulating fertilizer raw materials reduces nutrient loss and improves fertilization uniformity. In mineral processing, granulation optimizes the material's smelting properties. Its core function is to precisely control the granulation process to meet the specific material form requirements of various industries, making it a crucial link between raw material processing and finished product production.
Among granulation equipment types, drum granulators and pan granulators are two common types. Drum granulators utilize an inclined, rotating drum to continuously tumble the material within the drum due to gravity and friction. Combined with a sprayed binder, the drum granulator achieves agglomeration and granulation. It is suitable for large-scale production and is particularly effective in the production of compound fertilizers, organic fertilizers, and other fertilizers. It features high throughput and high granule strength. The disc granulator rotates an inclined disc and uses the synergistic effect of centrifugal force, gravity and friction to form particles at the edge of the disc, making it easy to observe the granulation process. The particles have good sphericity and are often used in laboratory tests or small and medium-sized production. They are more common in particle preparation in the fields of ceramics, catalysts, etc.

-
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Compound Fertilizer Production Line The efficiency of the Compound Fertilizer Production Line is influenced by various factors, which can significantly impact production output, quality, and overall operational costs. Understanding these factors is crucial for man...
READ MORE -
The capacity of a compound fertilizer production line plays a crucial role in determining its operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall productivity. Understanding how to calculate and select the right capacity is essential for manufacturers looking to meet market demand while maintain...
READ MORE -
Establishing a compound fertilizer production line is a complex task that requires careful planning, proper site selection, and construction of the right facilities. This involves evaluating the physical space, technical infrastructure, environmental factors, and ensuring compliance with regulations...
READ MORE
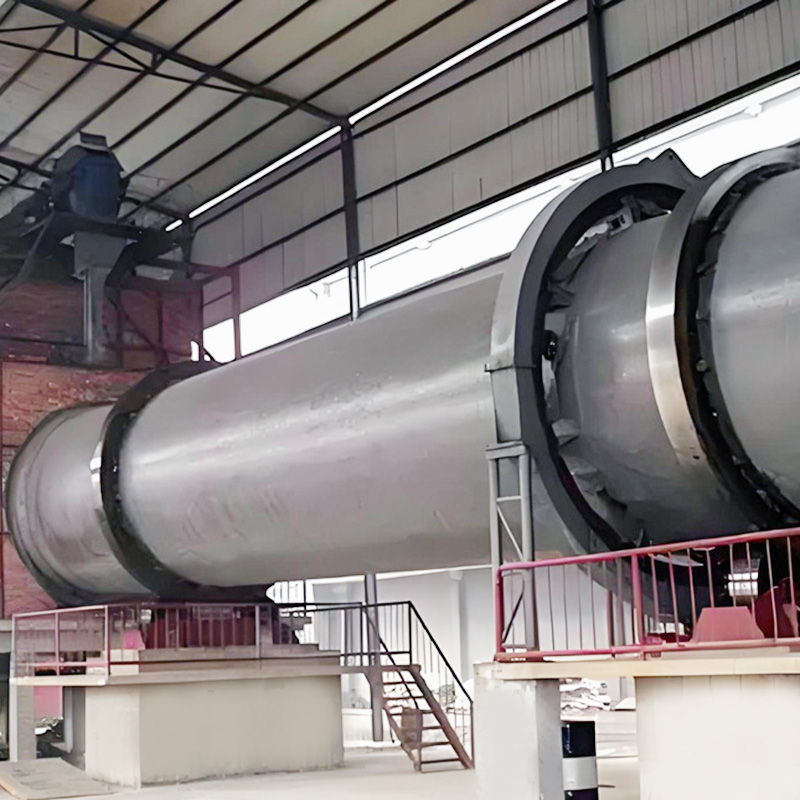
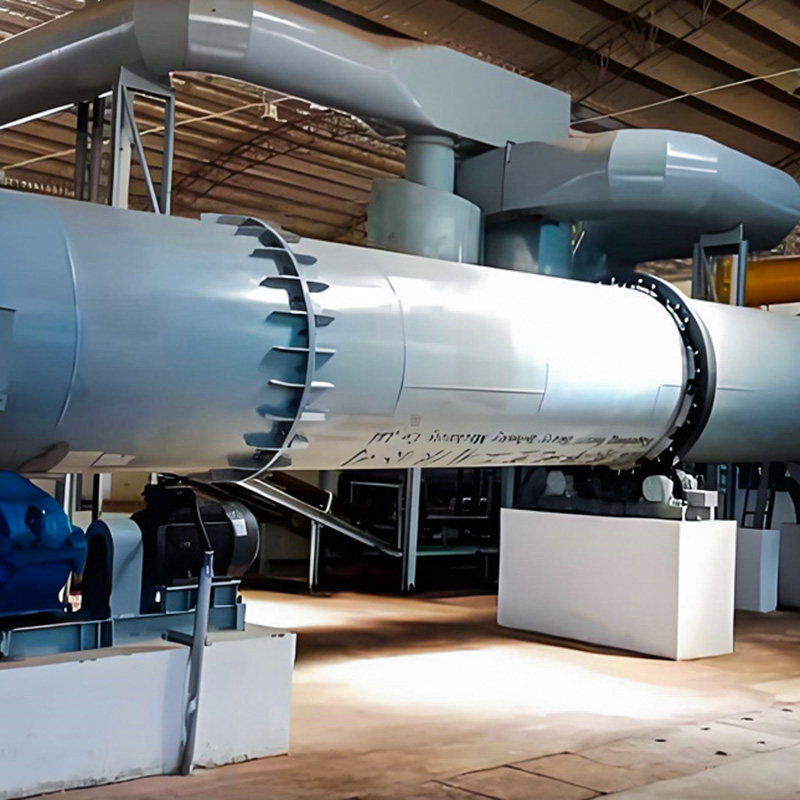
Fertilizer Granulation Equipment is used to convert powdered or semi-moist fertilizer materials into uniform, transportable, and storage-stable granules. This category includes equipment commonly applied in compound fertilizer, organic fertilizer, and BB fertilizer production lines. Fertilizer Granulation Equipment supports stable shaping, controlled particle size, and continuous processing, ensuring that the final granules meet industrial requirements for strength, density, and handling.
Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., experienced in the design and manufacturing of fertilizer machinery since 2007, provides multiple granulation solutions used in complete fertilizer production lines. Equipment such as drum granulators, rotary drums, and related auxiliary systems are applied in large chemical fertilizer facilities and integrated with drying, cooling, coating, crushing, and dust collection technologies.
1. Core Functions and Performance Features
-
Granulation and densification:Transforms loose materials into mechanical or agglomerated granules.
-
Particle size control:Allows adjustment through drum speed, angle, spray volume, or mixer configuration.
-
Continuous large-scale output:Supports stable production for NPK, organic, and special fertilizers.
-
Integration capability:Works with dryers, coolers, coating machines, conveyors, and dust collectors for complete line operation.
2. Main Types of Fertilizer Granulation Equipment & Working Principles
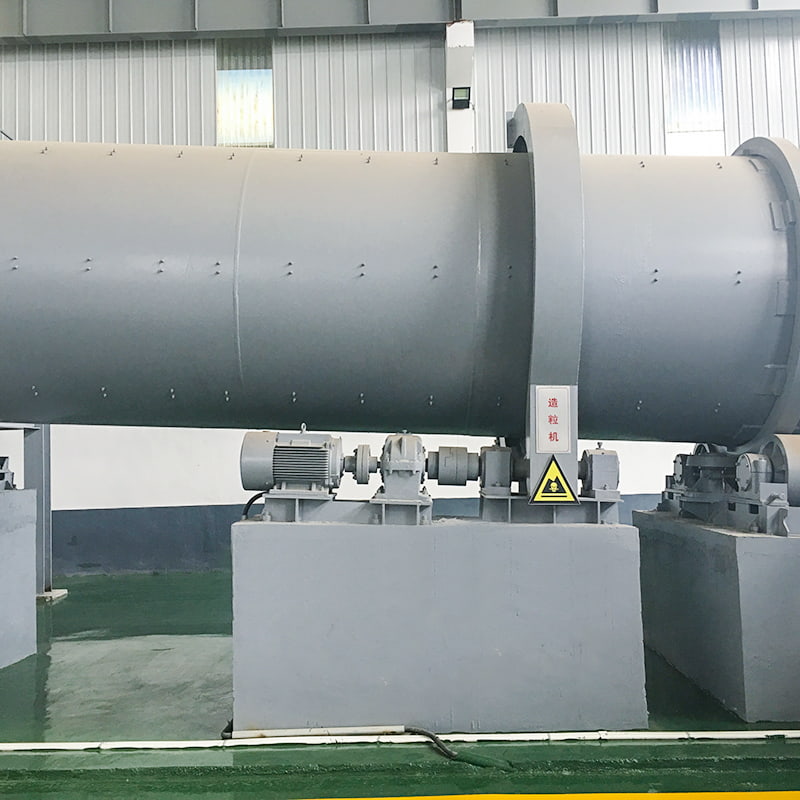
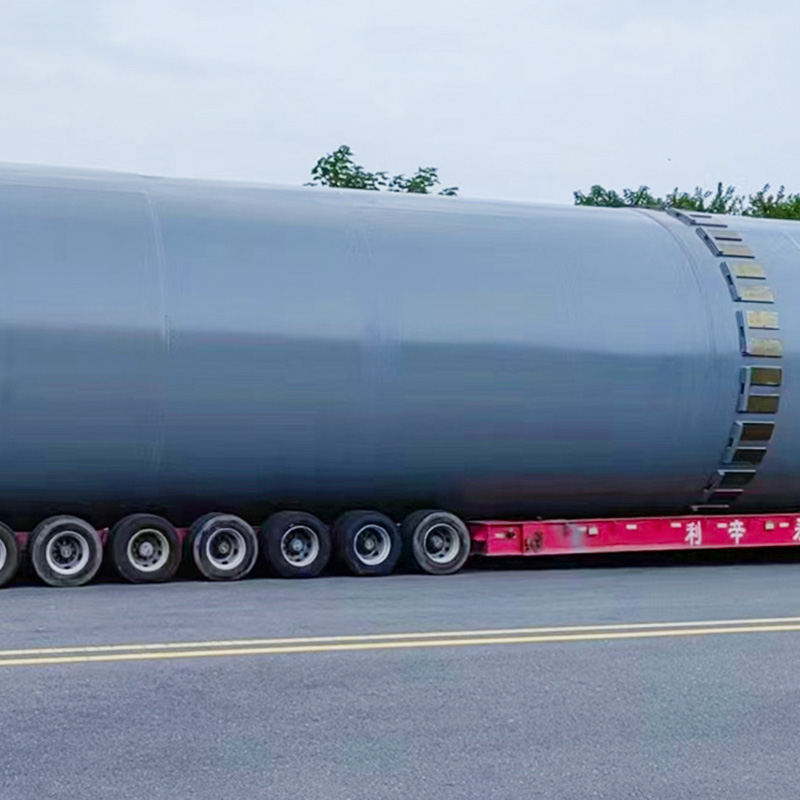
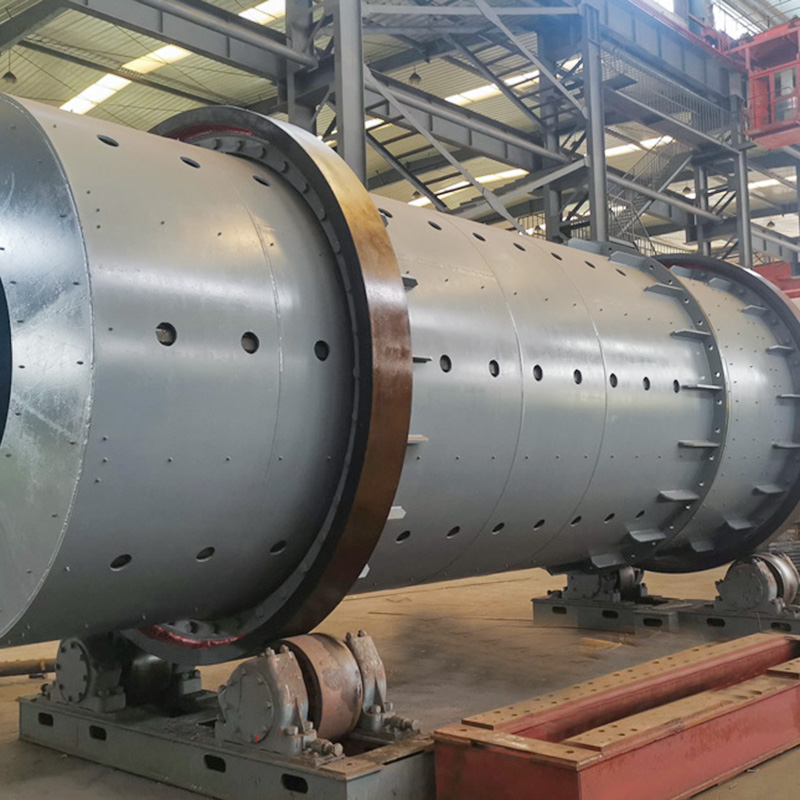
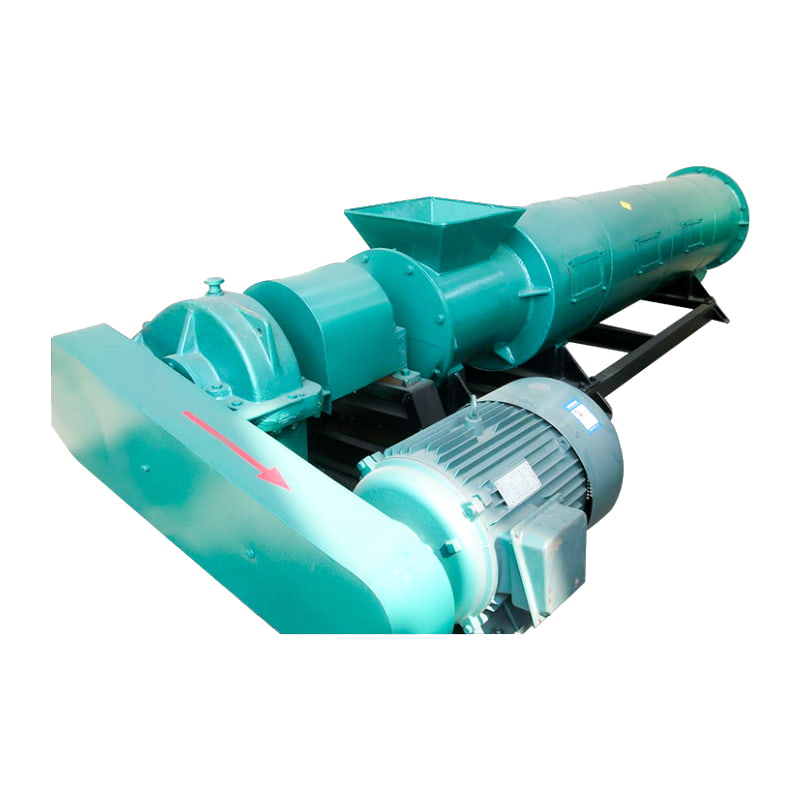
(1) Drum Granulator (Rotary Drum Granulation)
Working principle:Uses rotating drum motion to agglomerate moist raw materials through rolling and layering. Water or steam is sprayed to promote adhesion and pellet formation.
Typical applications:Large NPK compound fertilizer production lines.
Advantages:High output capacity, stable operation.
Limitations:Granule uniformity is influenced by material moisture and drum angle.
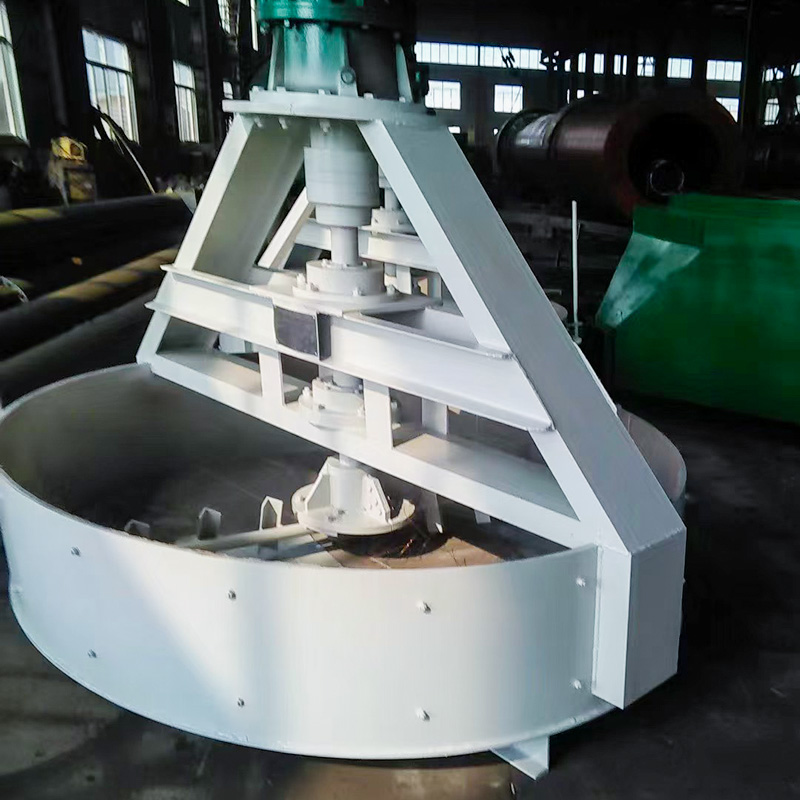
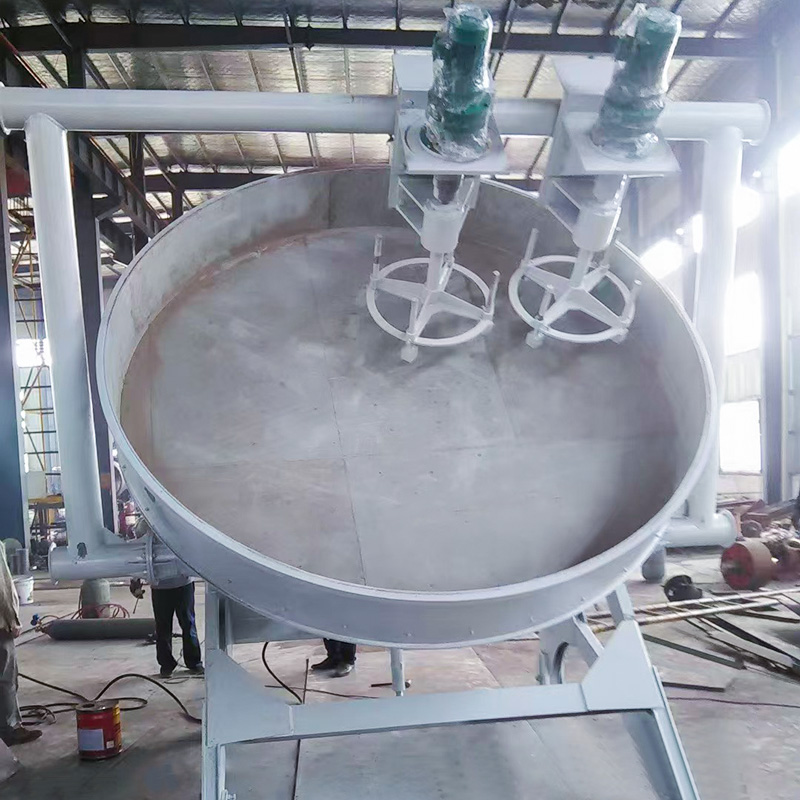
(2) Disc Granulator (Pan Granulation)
Working principle:Raw materials are fed onto a rotating inclined disc, where particles gradually agglomerate through rolling and layering.
Applications:Organic fertilizer, small/medium compound fertilizer lines.
Advantages:Flexible particle size control.
Limitations:Lower output compared with drum granulation.
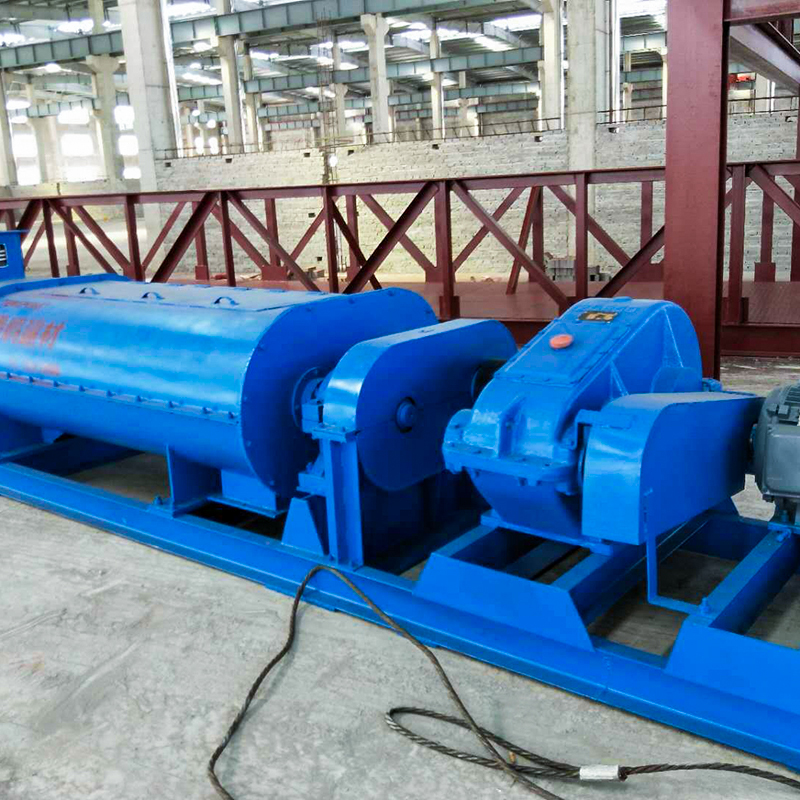
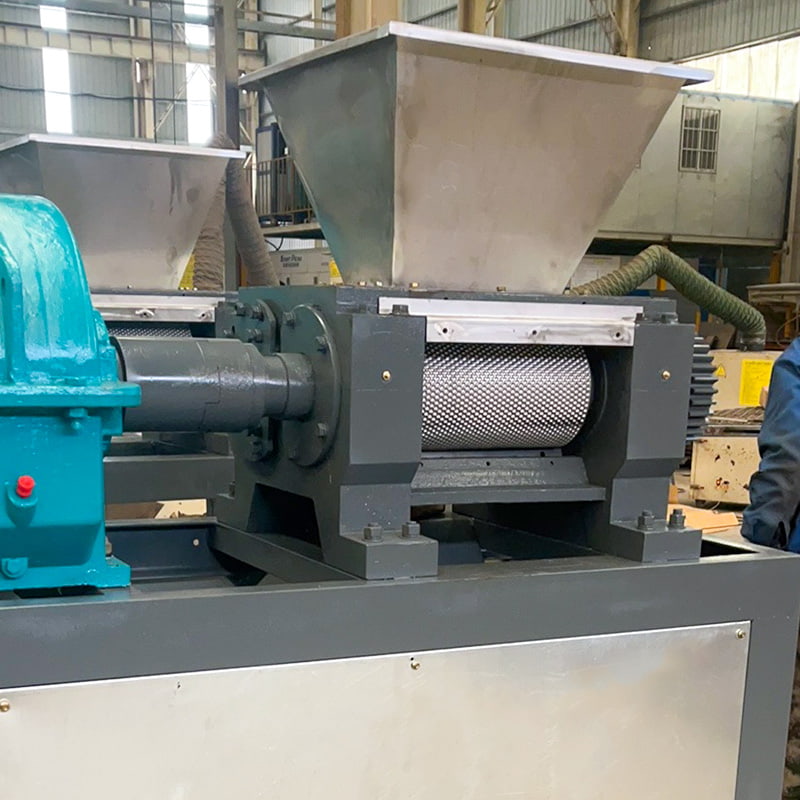
(3) Double Roller Granulator (Extrusion Granulation)
Working principle:Powdered fertilizers are compressed between rollers to form granules without heat or moisture.
Applications:Moisture-sensitive NPK, highly controlled formula fertilizers.
Advantages:Low energy consumption, no drying required.
Limitations:Suitable mainly for dry materials.
(4) Organic Fertilizer Special Granulator (Stirring Tooth or Wet Granulation)
Working principle:Uses high-speed stirring teeth to achieve granulation with fibrous or organic materials.
Applications:Composted organic fertilizer, manure-based fertilizer.
Advantages:Handles high-viscosity organic matter effectively.
Limitations:Requires pre-fermentation and moisture control.
3. Equipment Comparison Table
| Equipment Type | Granulation Method | Suitable Materials | Output Scale | Moisture Requirement | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drum Granulator | Rolling agglomeration | NPK, chemical fertilizers | Large | Medium–high | High capacity, continuous operation |
| Disc Granulator | Layer rolling | NPK, organic | Small–medium | Medium | Flexible particle size control |
| Double Roller Granulator | Mechanical extrusion | Dry powders | Medium | Low/no moisture | No-drying, low energy |
| Organic Fertilizer Granulator | Stirring/wet granulation | Organic & fibrous | Medium | High | Suitable for organic materials |
4. Maintenance & Operation Guidelines
-
Moisture control:Maintaining proper moisture levels ensures stable granulation; follow recommended ranges for each equipment type.
-
Regular drum/pan cleaning:Prevents material buildup that affects granule uniformity.
-
Roller surface inspection(for double roller granulators):Check wear patterns to maintain consistent pellet shape.
-
Lubrication:Periodically lubricate bearings, reducers, and transmission components.
-
Alignment checks:Verify drum inclination, disc angle, and roller spacing.
-
Dust management:Use suitable dust collectors to maintain clean operation and protect downstream equipment. Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. supplies dust collection solutions compatible with granulation lines.
5. Application Cases
-
Large NPK compound fertilizer lines using rotary drum granulation combined with dryers, coolers, and coating machines.
-
Organic fertilizer plants applying stirring-tooth granulators after fermentation processes.
-
BB fertilizer systems integrating granulators with material batching and conveying equipment.
-
Potassium sulfate and specialty fertilizer lines using extrusion granulation for precise formulations.
6. FAQ – Fertilizer Granulation Equipment
Q1: How to choose the appropriate granulation method?
A: Choose based on material moisture, formulation characteristics, desired capacity, and required granule strength.
Q2: What particle size range is typical?
A: Most lines produce 2–5 mm granules; adjustable depending on equipment settings.
Q3: Can different granulators be combined in one line?
A: Yes, depending on the raw material and process design. For example, extrusion granulation can be paired with coating systems or cooling units.
Q4: How does granulator capacity affect production line selection?
A: Drum granulators are suitable for large-scale production (>10 t/h), while disc granulators serve medium-scale plants.
Q5: Do granulation systems require dust collection?
A: Yes. Dust collectors help maintain environmental compliance and protect equipment. Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. offers dust control devices used in fertilizer processing.

 En
En
 English
English  Français
Français  русский
русский  中文简体
中文简体  عربى
عربى  Español
Español