- Compound Fertilizer Production Line
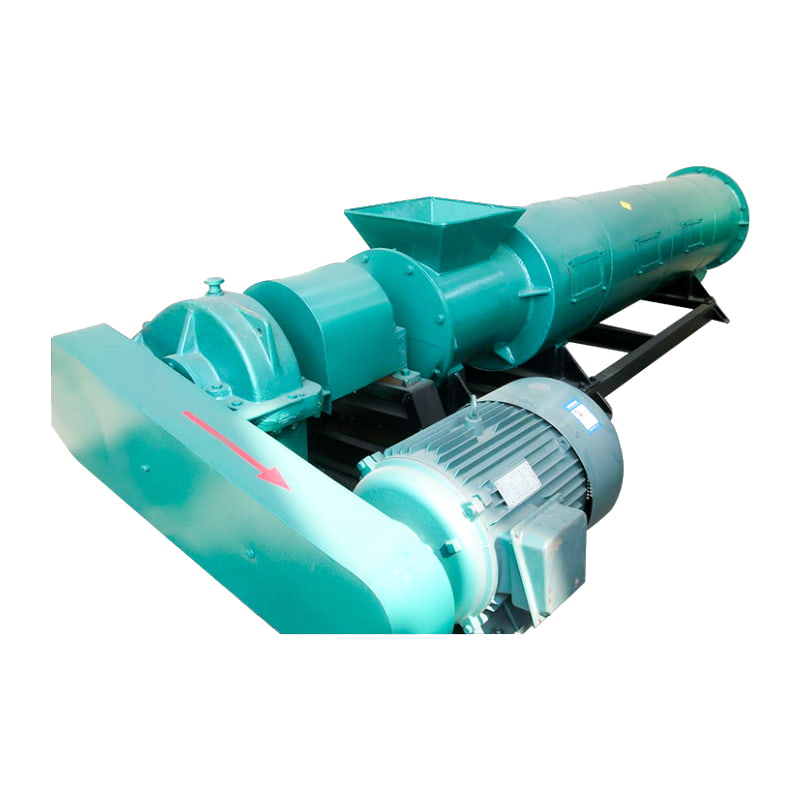
- Grinding Equipment
- Material Feeding Equipment
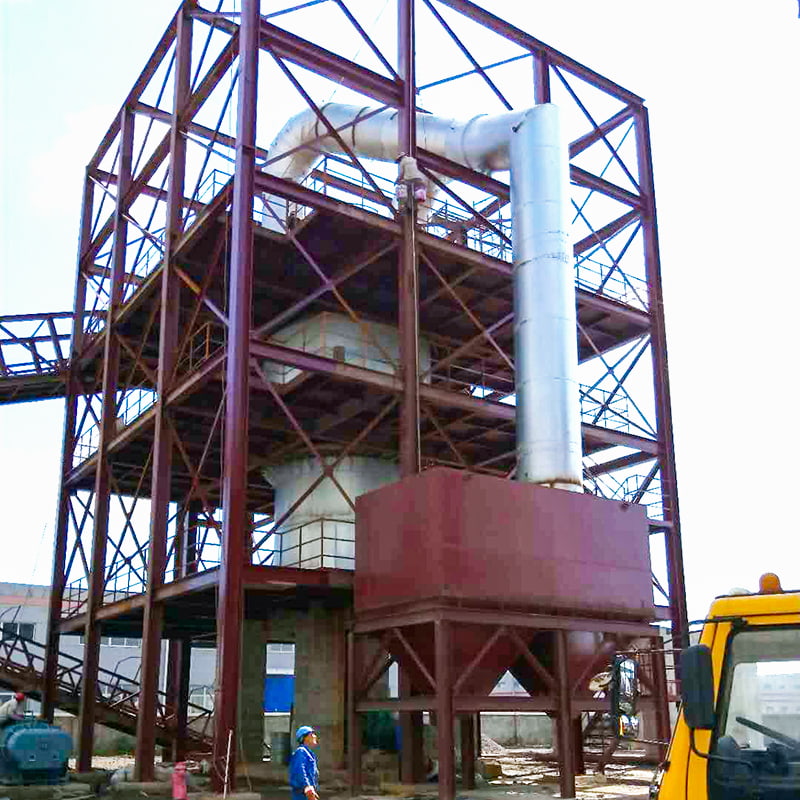
- Dust Collection Equipment
- Drying Equipment
- Conveying Equipment
- Elevating Equipment
- Crushing Equipment
- Screening Equipment
- Industrial Mixing and Agitation Equipment
- Granulation Equipment
- Calcination Equipment
- Cooling Equipment
- Bulk and Packaging Equipment
Calcination Equipment Supplier
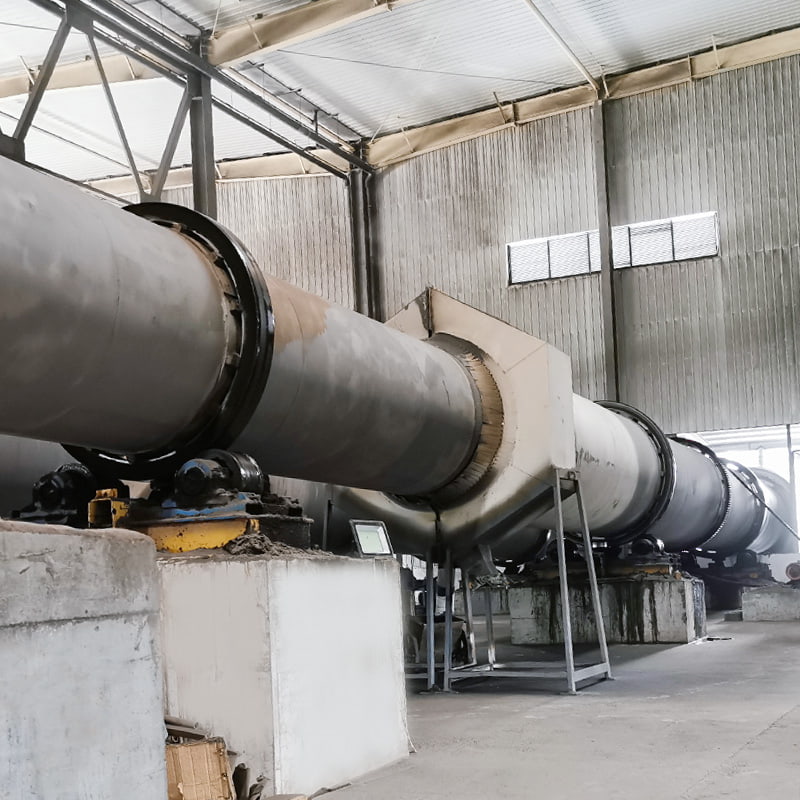
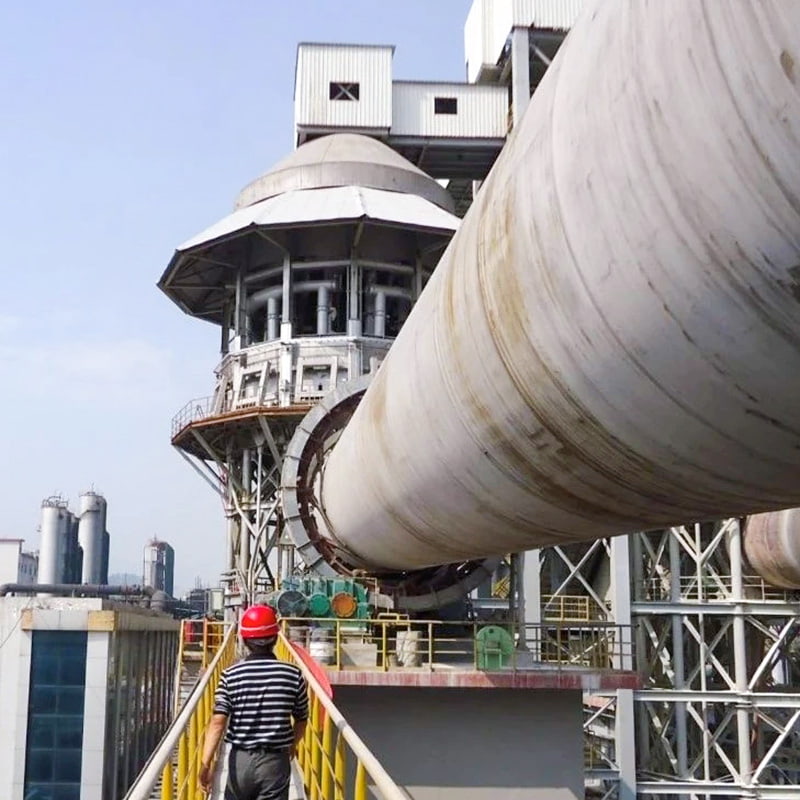
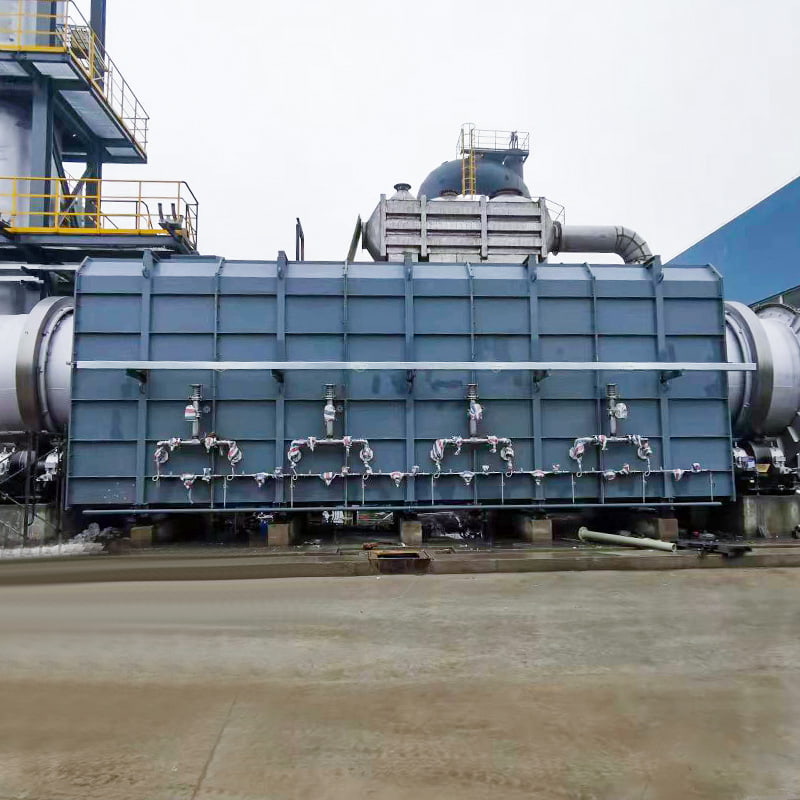
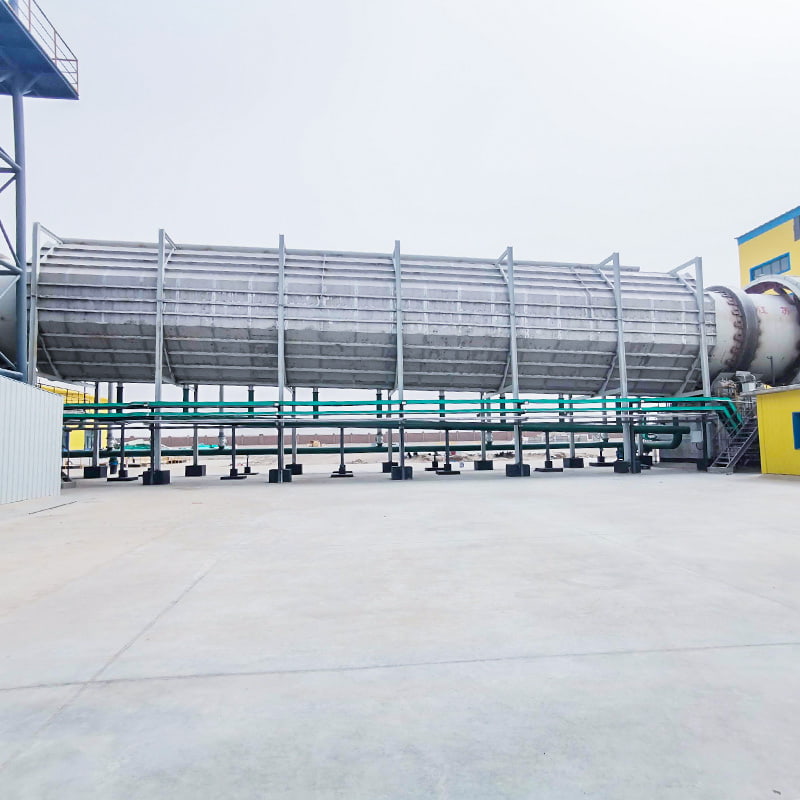
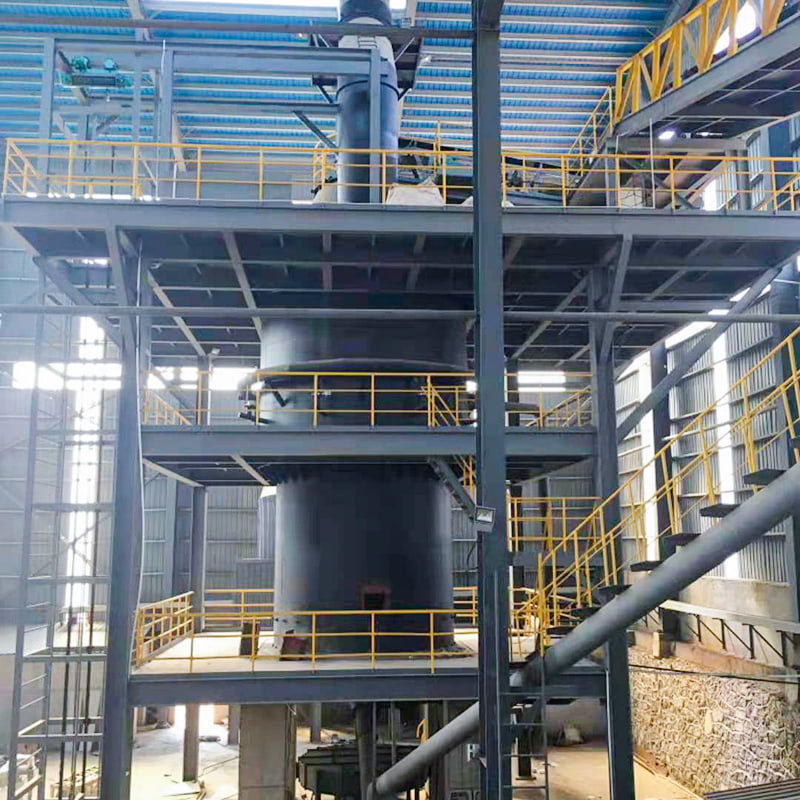
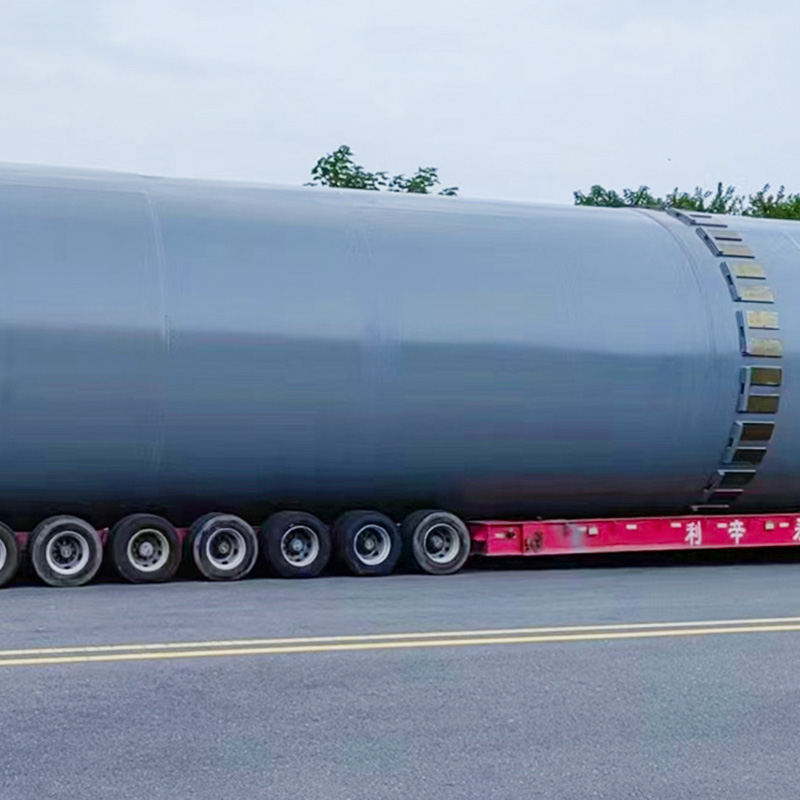
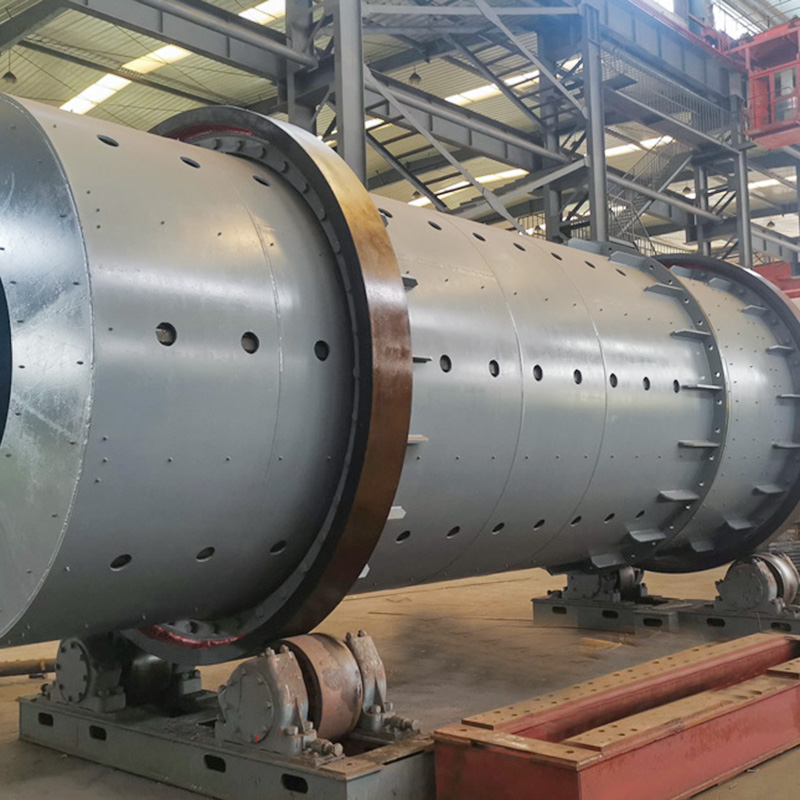
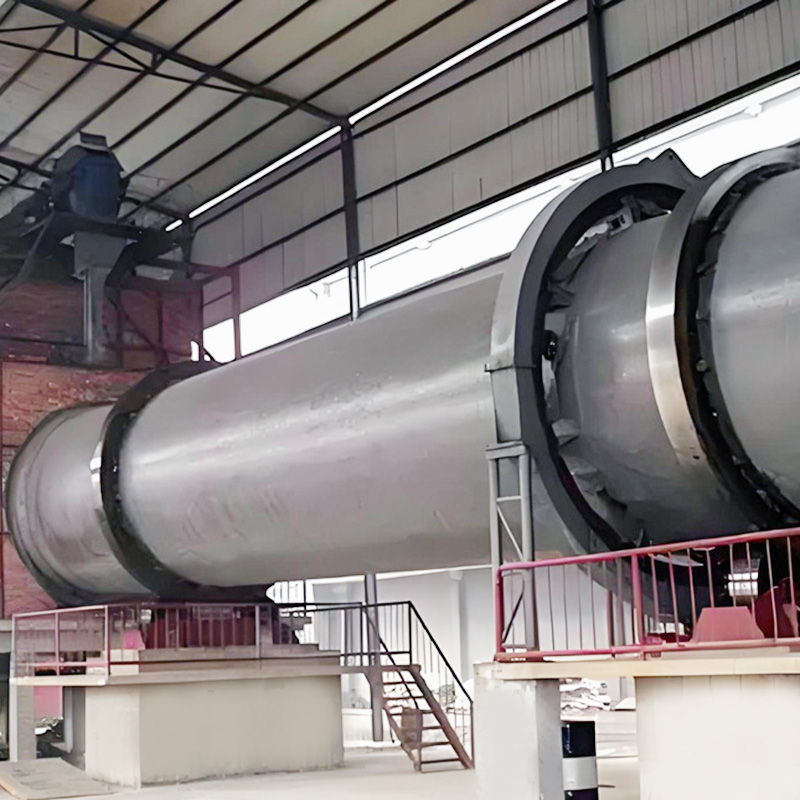
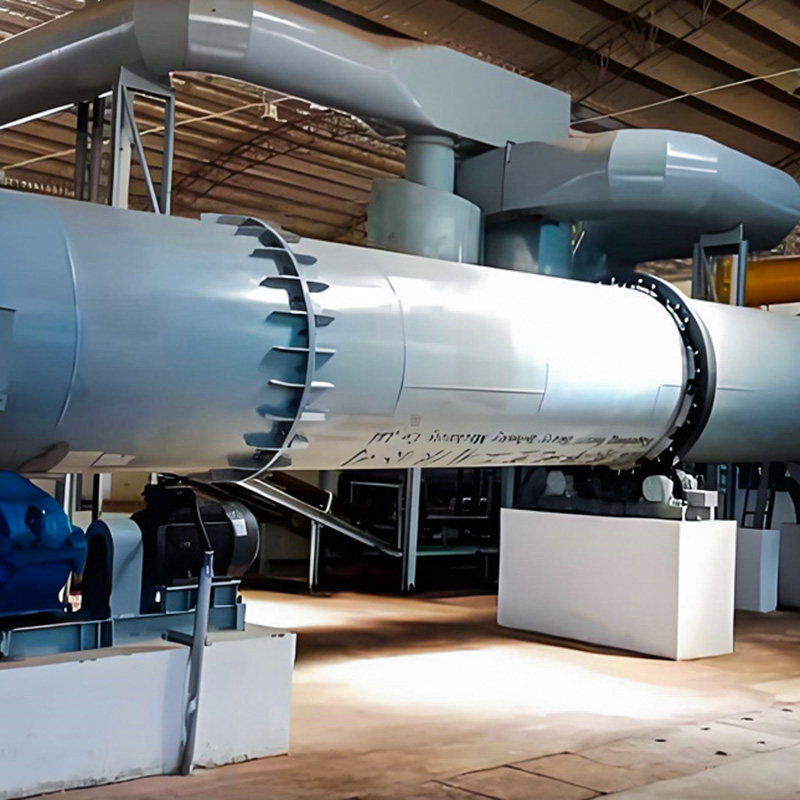
Calcination equipment is a type of industrial equipment used for high-temperature material processing. It uses direct or indirect heat sources to provide the required high-temperature environment for the material, promoting physical or chemical changes. Common types include rotary kilns and calciners. Rotary kilns are typically cylindrical and rotate slowly at a certain angle, allowing the material to tumble and move within them, ensuring even heating. Calcination furnaces can employ a variety of heating methods to meet the temperature and atmosphere requirements of different processes.
In the metallurgical industry, calcination equipment is used to roast ores, such as oxidative roasting of chromium and ferronickel ores, to improve their smelting properties. In the chemical industry, it can be used to treat catalyst materials to enhance their activity and stability. In building materials production, cement rotary kilns calcine raw materials into cement clinker, while lime rotary kilns are used to produce quicklime. Calcination equipment also plays an indispensable role in processing specialty materials, recovering rare metals, and treating solid and hazardous waste in the environmental protection sector, helping various industries achieve efficient and high-quality production goals.

-
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Compound Fertilizer Production Line The efficiency of the Compound Fertilizer Production Line is influenced by various factors, which can significantly impact production output, quality, and overall operational costs. Understanding these factors is crucial for man...
READ MORE -
The capacity of a compound fertilizer production line plays a crucial role in determining its operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall productivity. Understanding how to calculate and select the right capacity is essential for manufacturers looking to meet market demand while maintain...
READ MORE -
Establishing a compound fertilizer production line is a complex task that requires careful planning, proper site selection, and construction of the right facilities. This involves evaluating the physical space, technical infrastructure, environmental factors, and ensuring compliance with regulations...
READ MORE
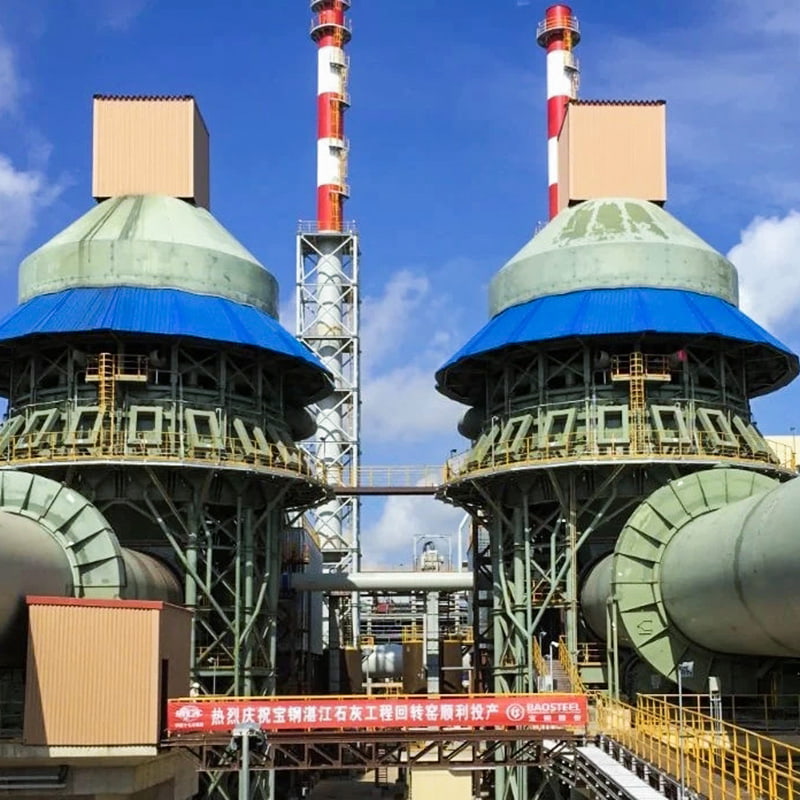
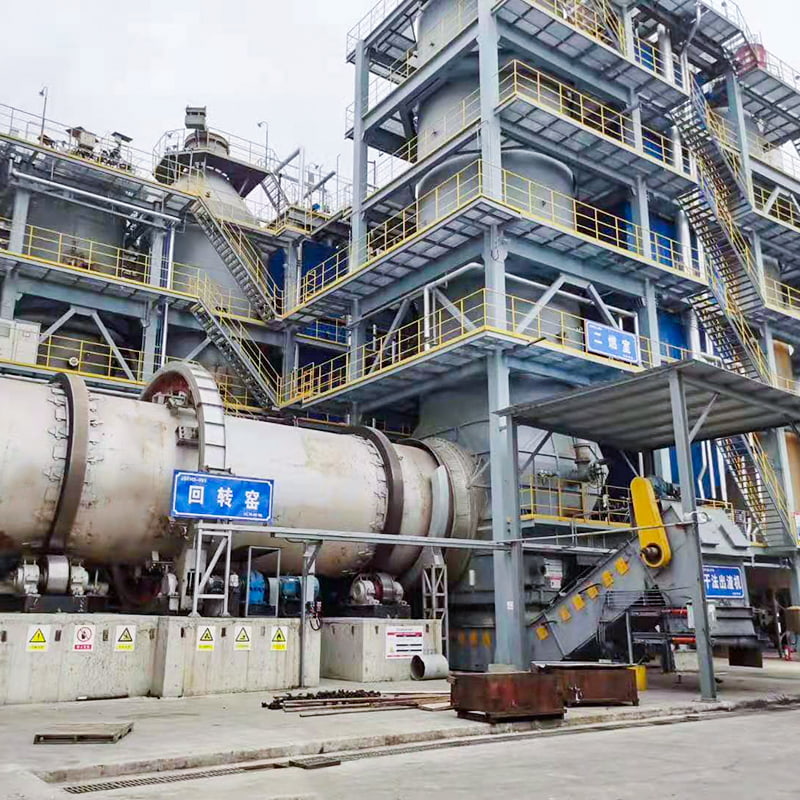
Calcination Equipment is widely applied in processes where materials require controlled thermal treatment to modify their physical or chemical properties. Typical functions include moisture removal, phase transformation, decomposition of carbonates, and preparation of active materials for subsequent processing steps. Calcination Equipment operates under high-temperature conditions with stable residence time, making it suitable for chemical fertilizers, building materials, mineral processing, and solid waste utilization. Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., with long-term experience in fertilizer machinery and building materials machinery, integrates these technologies into complete production lines used in compound fertilizers, organic fertilizers, potassium sulfate, and related industries.
Working Principles of Calcination Equipment
Different types of Calcination Equipment follow similar heat-transfer mechanisms but differ structurally:
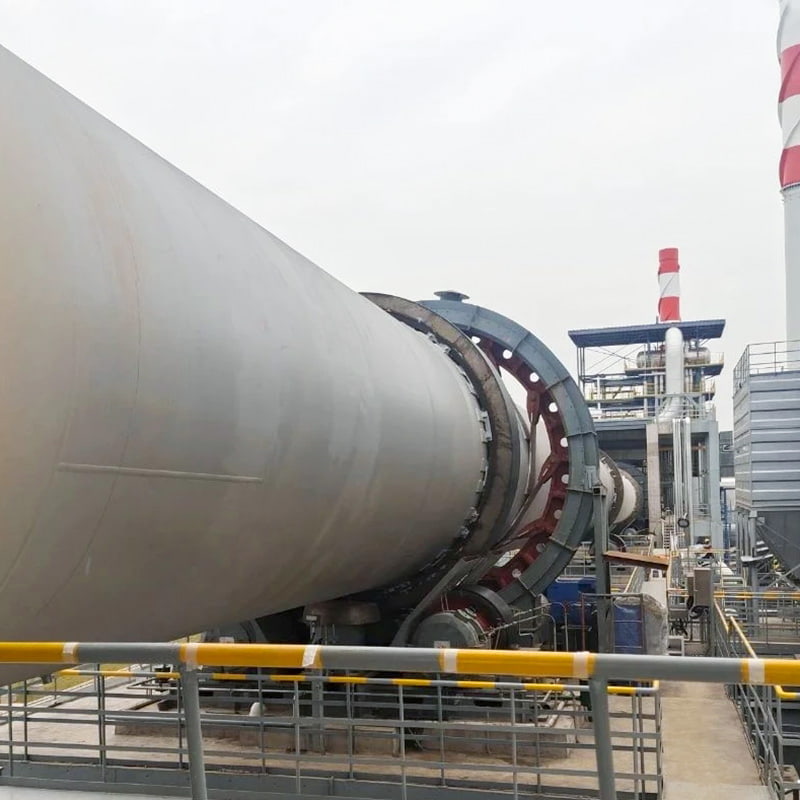
1. Rotary Kiln Calcination
-
Principle: Material enters a rotating cylindrical shell, where it is heated by direct or indirect combustion. Temperature control and residence time ensure uniform calcination.
-
Typical Applications: Fertilizer intermediates, clinker preparation, activated lime, refractory materials.
2. Fluidized Bed Calcination
-
Principle: High-velocity hot air forms a fluidized state, enhancing heat transfer and allowing precise temperature distribution.
-
Typical Applications: Fine powders, chemical catalysts, industrial salts.
3. Shaft Furnace Calcination
-
Principle: Material moves vertically in a packed bed while hot gases pass counter-currently, achieving energy-efficient calcination.
-
Typical Applications: Limestone, dolomite, metallurgical materials.
Application Cases
-
Fertilizer Industry: Rotary kiln systems used for calcining phosphate materials and potassium sulfate intermediates.
-
Building Materials: Calcination of cement raw materials and lightweight aggregates.
-
Metallurgy: Shaft furnace equipment used for oxide preparation and reduction processes.
-
Chemical Industry: Fluidized bed calcination of catalysts and specialty chemical powders.
Category Comparison of Calcination Equipment
| Type | Heat Transfer Method | Suitable Materials | Key Features | Typical Capacity Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Kiln | Direct/Indirect heating | Granules, lumps | Wide adaptability, adjustable residence time | Medium–large |
| Fluidized Bed | High-efficiency convection | Fine powders | Uniform calcination, good temperature control | Medium |
| Shaft Furnace | Counter-current heat flow | Bulk solids | Lower energy consumption, compact layout | Medium–large |
Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. incorporates these equipment types into integrated calcination systems, combining dryers, coolers, dust collection units, and material conveyors to support continuous, stable production.
Maintenance & Operation Guidance
Daily Maintenance
-
Inspect refractory linings for cracks or wear.
-
Check burner operation, airflow, and temperature stability.
-
Confirm seal integrity at feed and discharge ends.
-
Ensure lubricants for support rollers, bearings, and drives are maintained.
Periodic Maintenance
-
Alignment inspection for rotary kilns to prevent shell deformation.
-
Cleaning of air distributor plates in fluidized bed units.
-
Replacement of worn grate plates or refractory components.
-
Calibration of temperature sensors and control systems.
FAQs – Calcination Equipment
Q1: How to determine suitable calcination temperature?
A: Temperature is selected based on material decomposition characteristics and required phase transformation. Laboratory tests or pilot data are typically used.
Q2: What affects the residence time in a rotary kiln?
A: Kiln inclination, rotational speed, material fill rate, and particle size distribution.
Q3: How does calcination equipment integrate with upstream and downstream systems?
A: Feeding, drying, calcination, cooling, and dust removal are combined into a continuous line. Companies such as Nantong Alisen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. supply matched granulators, dryers, coolers, conveyors, and dust collectors for complete system operation.
Q4: What dust control methods are used in calcination?
A: Typically includes cyclone separators, bag filters, and induced-draft systems designed according to material volatility and particle characteristics.

 En
En
 English
English  Français
Français  русский
русский  中文简体
中文简体  عربى
عربى  Español
Español